 eHealth information systems today are proprietary and often only serve one specific department within a healthcare facility. It means it is impossible to easily share data across one facility, never mind trying to share data across different facilities, or different countries. The EC-sponsored project Artemis (A Semantic Web service-based P2P Infrastructure for the Interoperability of Medical Information Systems - IST-1-002103-STP) addresses this important interoperability problem.
eHealth information systems today are proprietary and often only serve one specific department within a healthcare facility. It means it is impossible to easily share data across one facility, never mind trying to share data across different facilities, or different countries. The EC-sponsored project Artemis (A Semantic Web service-based P2P Infrastructure for the Interoperability of Medical Information Systems - IST-1-002103-STP) addresses this important interoperability problem.
For the interoperability of healthcare messages, messaging interfaces, or interface engines are used. Currently, the Health Level 7 (HL7) Version 2 Messaging Standard is the most widely implemented standard in healthcare. Unfortunately, HL7 V2 compliance does not imply direct interoperability between healthcare systems, because V2 has no explicit information model. Instead it has rather vague definitions for many data fields and it contains many optional fields. It offers great flexibility, but requires detailed bilateral agreements among the healthcare systems to achieve interoperability. Therefore HL7 Version 3 was developed, based on an object-oriented data model, called Reference Information Model (RIM), but that can not talk to HL7 V2.
Artemis project addresses these messaging problems and provides an interoperability platform where organizations keep their proprietary systems, but expose their functionality through web services. Web service technology is chosen in Artemis since web services use standard transports, encodings, and protocols to exchange information. After broad support of web services across businesses, computer systems are enabled to exchange data on any platform over the Internet with security and reliability support.
Yet, web services provide technical interoperability; they do not provide a mechanism for automatic processing of the message content received unless the sent and received messages conform to the same interface standard. Since it is not realistic to expect a globally unique healthcare message standard, we take an alternative approach and semantically annotate both web service functionality and the messages that web services exchange. An essential element in defining semantics of web services is domain knowledge. Medical informatics is one of the few domains to have considerable domain knowledge developed through standards. For example, HL7 standard categorizes events and defines messages in healthcare based on service functionality, which reflects the business logic. Artemis uses HL7 as a basis for defining both the service action semantics and the message semantics.
Artemis message exchange framework provides the exchange of meaningful clinical information among healthcare institutes through semantic mediation. To provide scalability and discovery of other mediators, Artemis has a P2P communication architecture which is shown in Figure 1. An ontology mapping tool is developed for mapping different health care ontologies one into other and then using the mapping definition produced for automatically translating message instances. The framework proposed is generic enough to mediate between any incompatible healthcare standards that are currently in use.
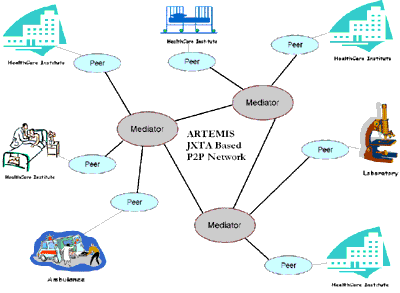 Figure 1. ARTEMIS Architecture
Figure 1. ARTEMIS Architecture
When it comes to discovery of web services, currently the most prominent web service registries are Universal Description, Discovery, Integration (UDDI) and electronic business XML (ebXML). There are also very recent efforts to use peer-to-peer (P2P) networks based on web services. However both service registries and P2P architectures available do not provide semantically enriched search capabilities. In the ARTEMIS project extensions are provided to these architectures to enable the discovery of web services based on their semantic descriptions.
Another crucial aspect in ARTEMIS is the ability to find and retrieve clinical information about a particular patient from different healthcare organizations where concrete sources are unknown. In most countries there are no unique person identifiers that would be valid for the whole lifetime of an individual and used by all parties in healthcare and for all episodes of care. On the contrary, in many cases several identifiers for a patient exist even within a single organization. Consequently a protocol is needed that allows for the identification of patients by means of non-unique patient-related attributes. This is a common problem in the healthcare sector that is likely to become very important with the increasing mobility of the workforce in Europe: locating and accessing prior clinical records for the continuity of care. Artemis developed a âPatient Identification Process Protocol (PIP)â and made this protocol available to healthcare systems through Web services.
Healthcare information systems operate within a strict regulatory framework that ensures the protection of personal data, outlines the conditions where processing is allowed. The Artemis project responded to these conditions by providing comprehensive security and privacy protection mechanisms. In Artemis, a process-based access control (PBAC) mechanism for web service authorisation has been developed. The security and privacy mechanisms developed for web services support virtual healthcare organisations by providing infrastructure based on web service standards along with dynamic authorisation mechanisms (PBAC) that enforce healthcare business process. PBAC provides a means of contextual and process oriented access control to enforce a business processes associated with a stateful resource model accessed through web service operations.
Coordinator contact details:
Prof. Dr. Asuman Dogac
Department of Computer Engineering
Director of Software Research & Development Center
Middle East Technical University
06531, Ankara, Turkey
http://www.srdc.metu.edu.tr/~asuman
Phone: +90 - 312 - 210 5598 or +90 - 312 - 210 2076
Fax: +90 - 312- 210 5572 or +90 - 312 - 210 1259
For further information, please visit:
http://www.srdc.metu.edu.tr/artemis/