The new Axiom Artis dBA Twin radiography system offers flexibility across the entire application spectrum, from neuroradiological and abdominal examinations, to pediatric applications requiring low dose. The unit is equipped with two 30 x 40 flat detectors. The modern biplanar flat detector technology delivers excellent detail resolution that supports physician decision-making in diagnostics and interventions. The biplanar system enables fast display of the anatomy in two planes, providing accurate work through simultaneous imaging. The system also supports the physician's workflow through programmable detector positioning and intelligent collision protection.
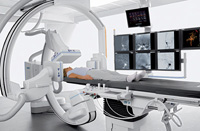 Angiography and syngo DynaCT
Angiography and syngo DynaCT
With the optional syngo DynaCT, Axiom Artis dBA Twin achieves soft tissue differentiation comparable to computed tomography (CT) acquisitions. As a result, intracranial bleeding can be detected faster than ever before, and brain tissue can be displayed in greater detail than with conventional procedures. Using the latest version of syngo DynaCT, which was introduced for the first time at the RSNA (Radiological Society of North America), in critical situations physicians receive clinically-relevant results of the highest possible resolution within one minute, supporting therapy decision-making. In addition, this method is used to check therapeutic measures. The advantage: the patient is not subjected to an additional computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) examination.
Innovative applications for neuroradiology as well as for abdominal and oncological interventions have been created with this technology. Through the continuous development and enhancement of syngo DynaCT, Siemens again confirms its leadership role in the industry. Last month, Siemens celebrated its 100th US syngo DynaCT installation at the Swedish Medical Center in Seattle, USA. This milestone attests not only to the popularity of this trendsetting technology, but also to its far-reaching implications for health care as a whole. To date, the application has been installed some 260 times worldwide.
Siemens Medical Solutions of Siemens AG (NYSE: SI) is one of the world's largest suppliers to the healthcare industry. The company is known for bringing together innovative medical technologies, healthcare information systems, management consulting, and support services, to help customers achieve tangible, sustainable, clinical and financial outcomes. Recent acquisitions in the area of in-vitro diagnostics such as Diagnostic Products Corporation and Bayer Diagnostics mark a significant milestone for Siemens as it becomes the first full service diagnostics company. Employing more than 41,000 people worldwide and operating in over 130 countries, Siemens Medical Solutions reported sales of 8.23 billion EUR, orders of 9.33 billion EUR and group profit of 1.06 billion EUR for fiscal 2006 (Sept. 30). Further information can be found by visiting http://www.siemens.com/medical